

Second equation:
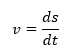
The speed is the derivative of the space divided by the derivative of the time.
Rearranging the equation, it stays:
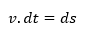
Which is a differential equation, so, integrating it, we have:

Replacing the value of  in the equation, we have:
in the equation, we have:
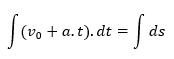
As we work with constant accelerations, the initial speed is a constant and the initial instant is equal to zero, we have:
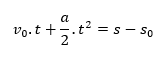
So,
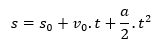
Which is the equation of the position, that is, the position of the body, it is the initial position of it added of its initial speed multiplied by the time, added of its acceleration divided by two multiply it by the time square. Don't worry too much about the results of the integer equations, because they run away from high school.
 Silêncio
Silêncio